Low cost service by operating Unmanned Aerial Vehicles for Mapping Projects
In the last years low-cost UAV Drones reached a level of practical reliability and professionalism which allow the use of these systems as mapping platforms. UAV based mapping provides not only the required accuracy with respect to cadastral laws and policies as well as requirements for the generation of elevation models in large-scale (map) such as gravel pits, UAVs are also competitive to other measurement technologies in terms of economic aspects.
Major advantages of UAVs compared to manned systems are that UAVs can fly in inaccessible areas, such as mountainous, volcanic, earthquake and desert areas, flood plains and scenes of accidents. Furthermore, most systems available on the market are stabilized and can operate autonomously. These systems are mainly low-cost systems, and thus a major advantage of UAVs is the cost factor, as UAVs are less expensive and have lower operating costs than manned aircrafts have.
SAKURA-GSR along with its UAV DRONE collaborator would undertake study SAKURA-GSR would bring in its Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing, GIS, and Software IT application experts to complete the study.
1. WORKFLOW
SAKURA Geoinformation Software Research Pvt.Ltd. (SAKURA-GSR) believes the first step in every UAV mapping project is to document the need for the study and status of permissions to fly UAVs for mapping.
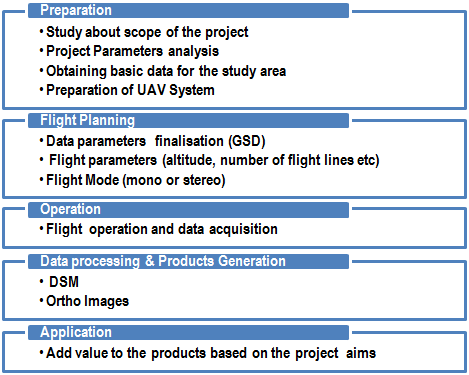
The workflow for UAV mapping is similar to the workflow of man-based aerial mapping systems. However, some elements of the workflow are different and thus, have been extended.
Figure 1. Workflow for UAV data acquisition and processing.
2. CHARACTERISTICS OF THE UAV SYSTEM
UAV is a small (38 inches wingspan) and ultra-light (maximum take-off weight of 1.7 pounds) platform made of flexible foam that performs precision aerial mapping missions thanks to the onboard GPS and the related flight management software that allows the operator to plan safely and efficiently a mission in 3D, and then monitor it in real-time. Thanks to the embedded camera, the UAV takes a collection of high-definition still images that are used later to generate maps and contour lines of the surveyed area.
The four main characteristics of the UAV are:
- a. Very light weight
- b. Electric-powered
- c. Semi-automatic flight
- d. Option for Manual control
Safety features:
- a. Pre-Flight automatic tests and procedures
- -Sensors calibration test
- -GPS signal test
- -Battery level test
- -Configuration of the Home point (altitude: 75 meters)
- b. In-Flight safety actions
- -Go to the Home Point
- -Emergency landing
- -Hold and Resume (air traffic management)
- -Restart Propeller
- c. Management of critical situations
- Barometer error – Go Home (using GPS altitude)
- -Way Out of working area (Strong wind) – Emergency Landing
- -Above working area – Go Home
- -Ground proximity – Hold and Resume
- -Wind too strong – Go Home
- -Low Battery – Go Home
- -Empty Battery – Propeller stopped and emergency landing
- -IMU error – Emergency landing
- -GPS signal loss – Emergency landing
Applications and added value of the UAV
Mapping applications with UAV may include agricultural applications, mining, construction and survey/GIS operations.
a. First, it brings safety to daily survey operations: there is no need for the humans to access dangerous working areas anymore (mines, quarries, or polluted sites). The missions can be programmed and reproduced reliably as often as needed for regularly updated maps.
b. Second, it is a cost-effective solution. It is cheaper to operate a UAS rather than an aircraft or other ground systems for the same results. Moreover, small can help Agriculture businesses and farmers face the growing needs of the population while reducing operational costs. It also enables the ability to take up new challenges -like water or environmental management through analysis of vegetation index maps.
c. Third, users can save time and work more efficiently. A mission does not need a long preparation time or long deployment constraints, or long waiting time for perfect weather conditions unlike, for example, the use of satellites. Initial results are accessible directly on-site, which is impossible with images provided by satellites or manned aircrafts.
d. It has social benefits too: it is eco-friendly (electric-powered), and its affordability allows many high-valued applications like data gathering for sustainability projects (agribusiness, reforestation) or post-disaster management missions.
e. Cadastre applications: Immediate benefit to various agencies, public as well as visitors etc. We can develop or interlink tools those will act as a guide for the landowners, lawyers, surveyors, valuer’s, real estate mangers, locals, and various civic/government authorities to locate the various facilities or assets. It acts as a base for the future multipurpose cadastral Information System and other GIS applications. Cadastre is the principal source of information about ownership of the land. The basic unit of the cadastre is the land parcel-Plot.
PROJECT BENEFITS
- Timely response to the client
- Better decision making
- Comprehensive information presentation
- Timely data update
- Reduced data redundancy
- Improved data accuracy
- Improved data consistency
- Improved data compatibility
- Improved data accessibility
- We train the client at desired place accepted by both the company and the customer.
- We also assure out best services
Links
- Flyer-ebee
- POC Anna University
- POC DRDO